Crowded roads in US city about to get worse as another fleet of self-driving cars is rolled out for testing
DRIVERS will soon have to make room on already-crowded roads for cars without anyone at the wheel – because there is no wheel.
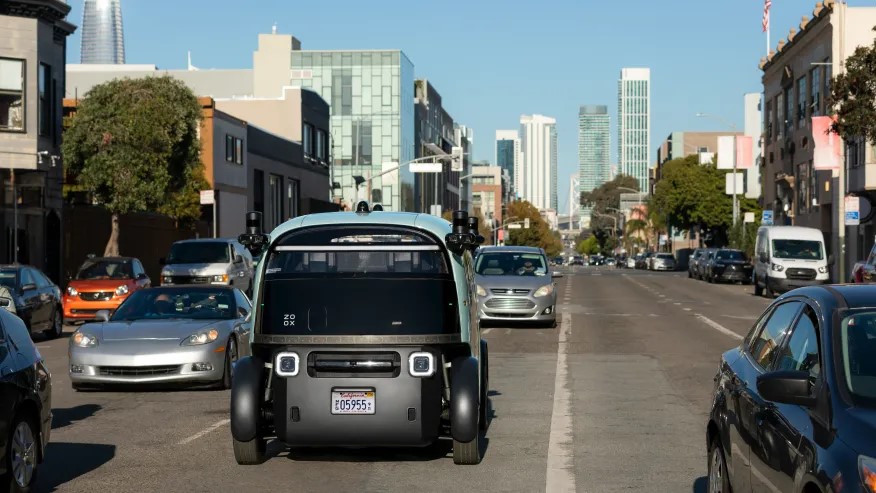
Driverless taxis are beginning to roll out on the streets of San Francisco, California.
Zoox, a transportation company owned by Amazon, announced new robotaxi tests on Monday.
The company called its automated vehicle a “purpose-built robotaxi.”
The cars have no steering wheels as four passengers face each other in train car-style seating.
Zoox said the pill-shaped vehicles have begun testing in San Francisco’s SoMa district.
READ MORE ON DRIVERLESS CARS
“This marks our entrance with the robotaxi into our second commercial market,” said Aicha Evans, the CEO of Zoox.
“Since 2017, our test fleet has autonomously navigated San Francisco streets with a safety driver.
“Now that we’ve passed all critical safety measures, we are excited to begin testing our robotaxi in this wonderful city.”
During the initial testing phase in SoMa, rides won’t be available to the public.
However, Zoox employees can take rides for testing and research purposes.
The company said in a blog post that workers who take rides will be “helping to refine the experience.”
I only want to use ‘quiet’ self-driving cars after taking a Waymo – there’s just a minor issue
Zoox has also started to test its driverless vehicles near the company’s headquarters in Foster City, California, and around the Las Vegas Strip.
The cars were built for self-driving and have no traditional manual controls.
“Zoox is the only company driving a purpose-built robotaxi on public roads without traditional manual controls,” Jesse Levinson, Zoox’s co-founder and CTO, said.
“This expansion marks our third city for our robotaxi operations, following Foster City and Las Vegas.
How do autonomous cars work?
Autonomous cars use sensors, algorithms, machine learning systems, and powerful processors.
They can create and maintain a map of the area around them based on several sensors situated in different parts of the car.
Radar sensors are used to keep track of the positions of other cars.
Video cameras can detect traffic lights, read road signs, track other cars, and look out for pedestrians.
A sophisticated software processes all of this information and plots a path for the car to take, sending instructions to the car’s actuators, which control acceleration, braking, and steering.
Hard-coded rules and object recognition help the software follow traffic rules and avoid obstacles.
Source: Synopsys
“We’ve rigorously tested and validated our AI stack in multiple cities over the last seven years in preparation for the deployment of our robotaxi fleet.
“From day one, our robotaxis will be leveraging a deep history and understanding of this area.”
As the testing continues, Zoox aims to expand its geofencing to roll out trials in other neighborhoods.
The U.S. Sun has reached out to Zoox for comment.
ZOOX VS WAYMO
On top of Zoox not featuring manual controls, passengers enter the car through sliding doors.
The design makes it unlike cars piloted by regular drivers – but other self-driving cars like Waymo use cars that are available commercially.
Waymo, once known as the Google Self-Driving Car Project, operates SUVs outfitted with sensors.
U.S. Sun staffer Ryan Cleary was extremely impressed with his Waymo experience last month as it operates in a handful of US states.
Read More on The US Sun
“I only want to use self-driving cars after taking a Waymo,” Cleary said.
“It was quiet, no driver bothered me with talking or their music choices.”